Twice around the tree algorithm.
If you’re looking for twice around the tree algorithm images information connected with to the twice around the tree algorithm keyword, you have visit the ideal site. Our website frequently provides you with suggestions for seeing the highest quality video and picture content, please kindly hunt and find more enlightening video articles and graphics that fit your interests.
 Algorithms Free Full Text A Linear Time Algorithm For The Isometric Reconciliation Of Unrooted Trees Html From mdpi.com
Algorithms Free Full Text A Linear Time Algorithm For The Isometric Reconciliation Of Unrooted Trees Html From mdpi.com
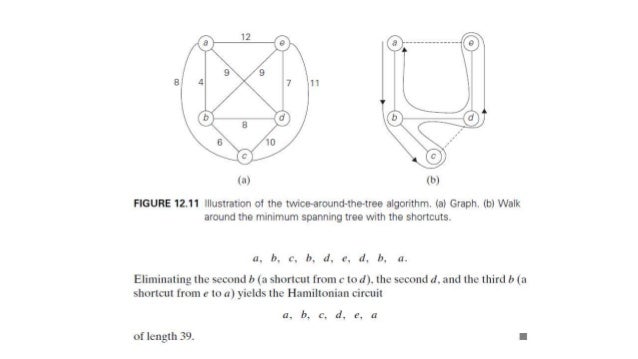
Twice Around the Tree Algorithm. Splitting can be done on various factors as shown below ie. Twice around the tree algorithm for TSP. Construct a Minimum Spanning Tree of the graph corresponding to a given instance of the TSP problem Step 2.
Its a recommended approach for picking path optimization due to the amount of time it takes and its accuracy level.
NP-completeness has stimulated research into the direction of approximation algorithms. Starting at an arbitrary vertex perform a walk around the minimum spanning tree recording all the vertices passed by. P exp -costs - costs T 2. Two states s and s 1. On a gender basis height basis or based on class.
 Source: pinterest.com
Source: pinterest.com
Among the most illustrious approximation algorithms for the Euclidean TSP is the twice around the tree heuristic which works as follows. Among the most illustrious approximation algorithms for the Euclidean TSP is the twice around the tree heuristic which works as follows. Volunteer scientific initiation student in Graph Theory field resulting in the paper Twice-around a Shortest-path Tree Significantly Increases the Solution Cost. Approximation Algorithm-TSP in Tamil Twice Around Tree Algorithm Daa Design and Analysis of AlgorithmIf you like the content of this Approximation Algori. Working of a Decision Tree Algorithm.
Step 1 Construct a minimum spanning tree of the graph corresponding to a given instance of the traveling salesman problem.
Step 1 Construct a minimum spanning tree of the graph corresponding to a given instance of the traveling salesman problem. Starting at an arbitrary vertex perform a walk around the minimum spanning tree recording all the vertices passed by. U uniformRandom 0 1 3. P exp -costs - costs T 2.
 Source: sciencedirect.com
Source: sciencedirect.com
Add edges in increasing weight skipping those whose addition would create a cycle. The first diagram is the given graph. P exp -costs - costs T 2. ExpCoinFlip s s Input.
 Source: pinterest.com
Source: pinterest.com
This can be done by a DFS traversal. U uniformRandom 0 1 3. Splitting It is the process of the partitioning of data into subsets. Twice-around-the Tree Algorithm Step 1.
 Source: slideshare.net
Source: slideshare.net
Starting at an arbitrary vertex perform a walk around the minimum spanning tree recording all the vertices passed by. Twice Around The Tree Algorithm February 17 2020 Get link. U uniformRandom 0 1 3. The paper reports the empirical performance comparison between the classical Twice-around algorithm and a modified Twice-around which uses Dijkstras shortest-path as sub-algorithm.
Proof We need to show that f s a 2 f s. There are many steps that are involved in the working of a decision tree. Twice around the tree algorithm for TSP. U uniformRandom 0 1 3.
U uniformRandom 0 1 3.
Twice around the tree algorithm for TSP. The twice around the minimum spanning tree is a 2-approximation algorithm for the traveling salesman with Euclidean distances. Consider the point when edge e uv is added. Construct a Minimum Spanning Tree of the graph corresponding to a given instance of the TSP problem Step 2. Following is the MST based algorithm.
 Source: mdpi.com
Source: mdpi.com
Twice-around-the-tree algorithm to approximate the traveling salesman problem. Twice-around-the-tree algorithm. Starting at an arbitrary vertex perform a walk around the minimum spanning tree recording all the vertices passed by. Splitting It is the process of the partitioning of data into subsets. ExpCoinFlip s s Input.
This algorithm uses a spanning tree to find an optimal route by generating a list of vertices while walking around the spanning tree. Its a recommended approach for picking path optimization due to the amount of time it takes and its accuracy level. Kruskals Algorithm Kruskals Algorithm. Step 1 Construct a minimum spanning tree of the graph corresponding to a given instance of the traveling salesman problem.
Splitting It is the process of the partitioning of data into subsets.
Following is the MST based algorithm. Starting at an arbitrary vertex perform a walk around the minimum spanning tree recording all the vertices passed by. In what manner is a state-space tree for a backtracking algorithm constructed. Step 1 Construct a minimum spanning tree of the graph corresponding to a given instance of the traveling salesman problem.
 Source: ru.pinterest.com
Source: ru.pinterest.com
This can be done by a DFS traversal. Intro To Algorithms Chapter 14 Red Black Trees Leaf It Up To Binary Trees Basecs Medium Frontiers Decision Tree For Early Detection Of Cognitive 4 Pathfinding And Graph Search Algorithms Graph. Splitting can be done on various factors as shown below ie. S2 Double every edge in the tree to get a Eulerian graph.
 Source: mdpi.com
Source: mdpi.com
Print the vertices and the length of the circuit. Splitting It is the process of the partitioning of data into subsets. ExpCoinFlip s s Input. Step 1 Construct a minimum spanning tree of the graph corresponding to a given instance of the traveling salesman problem.
 Source: pinterest.com
Source: pinterest.com
V u S nodes to which v has a path just before e is added u is in V-S otherwise there would be. Twice around the tree algorithm for TSP. Construct a Minimum Spanning Tree of the graph corresponding to a given instance of the TSP problem Step 2. ExpCoinFlip s s Input.
Twice Around the Tree Algorithm.
2 Construct MST from with 1 as root using Prims Algorithm. Twice-around-the-tree algorithm to approximate the traveling salesman problem. Two states s and s 1. Among the most illustrious approximation algorithms for the Euclidean TSP is the twice around the tree heuristic which works as follows. Twice-around-the Tree Algorithm Step 1.
 Source: pinterest.com
Source: pinterest.com
Twice Around the Tree Algorithm. Consider the point when edge e uv is added. The solution given from this algorithm is NOT optimal nor is it necessarily possible. V u S nodes to which v has a path just before e is added u is in V-S otherwise there would be. Working of a Decision Tree Algorithm.
Twice-around-the Tree Algorithm Step 1.
ExpCoinFlip s s Input. Twice-around-the Tree Algorithm Step 1. The paper reports the empirical performance comparison between the classical Twice-around algorithm and a modified Twice-around which uses Dijkstras shortest-path as sub-algorithm. S1 Compute the minimum spanning tree of the cities.
 Source: mdpi.com
Source: mdpi.com
On a gender basis height basis or based on class. Twice Around the Tree Algorithm. S2 Double every edge in the tree to get a Eulerian graph. View Answer _____ enumerates a list of promising nodes that could be computed to give the possible solutions of a given problem.
 Source: ru.pinterest.com
Source: ru.pinterest.com
View Answer _____ enumerates a list of promising nodes that could be computed to give the possible solutions of a given problem. 3 List vertices visited in preorder walk of the constructed MST and add 1 at the end. Splitting It is the process of the partitioning of data into subsets. Approximation Algorithm-TSP in Tamil Twice Around Tree Algorithm Daa Design and Analysis of AlgorithmIf you like the content of this Approximation Algori.
 Source: pinterest.com
Source: pinterest.com
Twice-around-the-tree algorithm to approximate the traveling salesman problem. Two states s and s 1. In what manner is a state-space tree for a backtracking algorithm constructed. ExpCoinFlip s s Input.
Twice Around the Tree Algorithm.
Theorem Kruskals algorithm produces a minimum spanning tree. This can be done by a DFS traversal. Approximation Algorithm-TSP in Tamil Twice Around Tree Algorithm Daa Design and Analysis of AlgorithmIf you like the content of this Approximation Algori. Starting at an arbitrary vertex perform a walk around the minimum spanning tree recording all the vertices passed by. Volunteer scientific initiation student in Graph Theory field resulting in the paper Twice-around a Shortest-path Tree Significantly Increases the Solution Cost.
 Source: ru.pinterest.com
Source: ru.pinterest.com
Splitting can be done on various factors as shown below ie. Twice-around-the-tree algorithm to approximate the traveling salesman problem. Step 2 Starting at an arbitrary vertex perform a walk around the minimum spanning tree recording all the vertices passed by. The solution given from this algorithm is NOT optimal nor is it necessarily possible. This can be done by a DFS traversal.
ExpCoinFlip s s Input.
Consider the point when edge e uv is added. V u S nodes to which v has a path just before e is added u is in V-S otherwise there would be. There are many steps that are involved in the working of a decision tree. 1 Let 1 be the starting and ending point for salesman.
 Source: pinterest.com
Source: pinterest.com
Following is the MST based algorithm. Among the most illustrious approximation algorithms for the Euclidean TSP is the twice around the tree heuristic which works as follows. Splitting It is the process of the partitioning of data into subsets. Starting at an arbitrary vertex perform a walk around the minimum spanning tree recording all the vertices passed by. NP-completeness has stimulated research into the direction of approximation algorithms.
 Source: youtube.com
Source: youtube.com
Starting at an arbitrary vertex perform a walk around the minimum spanning tree recording all the vertices passed by. Construct a Minimum Spanning Tree of the graph corresponding to a given instance of the TSP problem Step 2. ExpCoinFlip s s Input. Theorem Kruskals algorithm produces a minimum spanning tree. Working of a Decision Tree Algorithm.
 Source: slideshare.net
Source: slideshare.net
Twice-around-the-tree algorithm to approximate the traveling salesman problem. 2 Construct MST from with 1 as root using Prims Algorithm. Examined twice so duplicate checking is not necessary. S2 Double every edge in the tree to get a Eulerian graph. Approximation Algorithm-TSP in Tamil Twice Around Tree Algorithm Daa Design and Analysis of AlgorithmIf you like the content of this Approximation Algori.
This site is an open community for users to share their favorite wallpapers on the internet, all images or pictures in this website are for personal wallpaper use only, it is stricly prohibited to use this wallpaper for commercial purposes, if you are the author and find this image is shared without your permission, please kindly raise a DMCA report to Us.
If you find this site good, please support us by sharing this posts to your favorite social media accounts like Facebook, Instagram and so on or you can also bookmark this blog page with the title twice around the tree algorithm by using Ctrl + D for devices a laptop with a Windows operating system or Command + D for laptops with an Apple operating system. If you use a smartphone, you can also use the drawer menu of the browser you are using. Whether it’s a Windows, Mac, iOS or Android operating system, you will still be able to bookmark this website.





